What Are Brake Pads? What Do They Do?
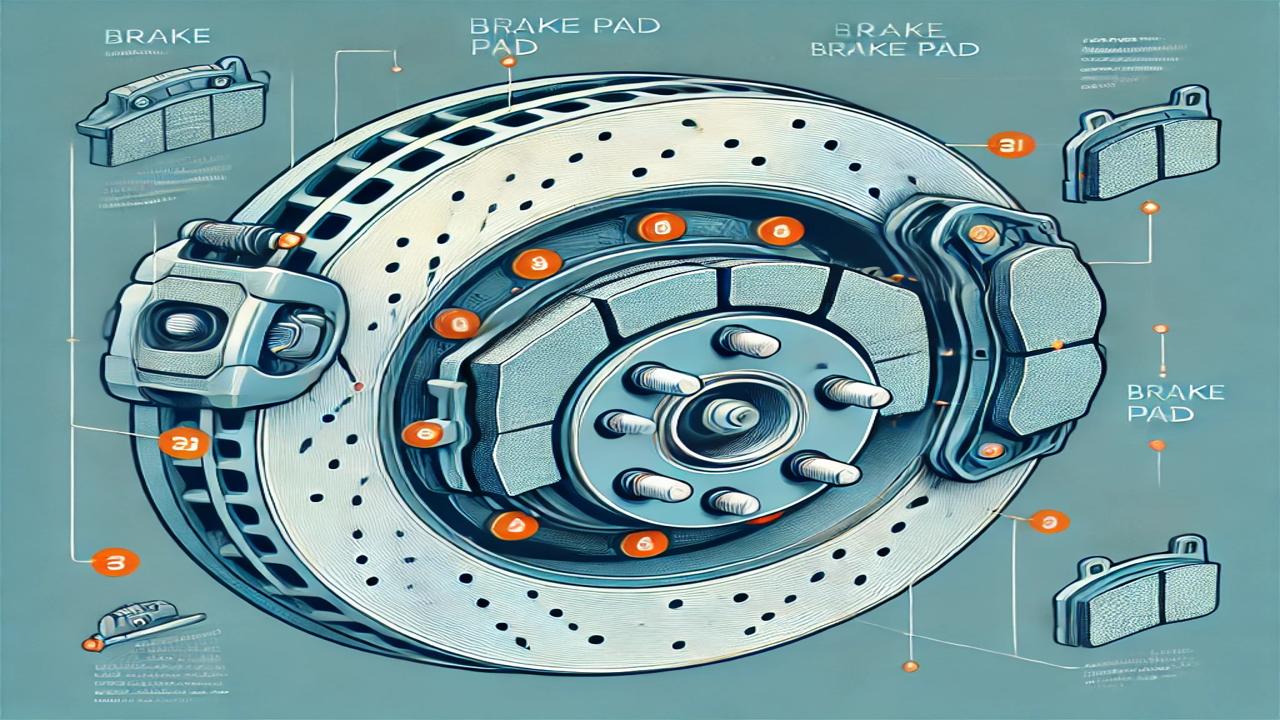
Brake pads are an essential component in a vehicle's braking system, responsible for slowing down or stopping the vehicle by creating friction during braking. They play a critical role in ensuring the vehicle's safe stopping ability, directly affecting road safety. Brake pads are designed to withstand high temperatures, especially in vehicles carrying heavy loads or those driving at high speeds.
What Are Brake Pads?
Brake pads are components that press against the brake disc to create friction, which helps slow down or stop the vehicle. Most vehicles use a disc brake system, with the brake pad being the crucial part of this system. Made of materials like metal, ceramic, or organic compounds, the brake pad generates friction against the disc to convert kinetic energy into heat, reducing the vehicle’s speed.
How Do Brake Pads Work?
-
Stopping the Vehicle: The primary function of the brake pad is to stop the vehicle. When the driver presses the brake pedal, the brake pads press against the brake disc, converting kinetic energy into heat and decelerating the car.
-
Slowing Down the Vehicle: Brake pads maintain constant contact with the brake discs, allowing the vehicle to gradually slow down, ensuring controlled deceleration.
-
Providing Braking Force: Brake pads are crucial in providing the necessary braking force for a safe stop. They work with the rest of the braking system to ensure the highest level of safety.
-
Heat Distribution: During braking, brake pads produce a significant amount of heat. The material of the pads plays a role in distributing this heat. Organic pads are more heat resistant, while ceramic pads tend to perform better at higher temperatures.
Types of Brake Pads
Brake pads come in different types based on the materials they are made from:
-
Organic Brake Pads: These are made from a mix of carbon, rubber, resin, and metal components. They are generally quieter and produce less dust but wear out faster and can lose efficiency at higher temperatures.
-
Metallic Brake Pads: These pads are made from metal alloys, including iron, copper, and steel. They are known for their high heat resistance and are ideal for heavy-duty vehicles but tend to produce more noise and dust.
-
Ceramic Brake Pads: Ceramic pads are durable and offer high performance. They handle heat well and are typically quieter with lower dust production, although they tend to be more expensive.
When Should Brake Pads Be Replaced?
Brake pads wear down over time and need replacement to maintain performance. Some signs that your brake pads may need to be replaced include:
-
Squealing Noises: If you hear metallic squealing while braking, it's a sign that the pads are worn down and need replacing.
-
Decreased Braking Response: If the brake pedal feels softer or requires more pressure, or if the stopping distance increases, it may indicate worn brake pads.
-
Weak Brake Engagement: If the vehicle doesn't stop effectively or the braking feels less responsive, the brake pads may be past their prime.
-
Faster Wear: If the pads are exposed to high temperatures frequently, they can wear down quicker. Regular replacement is necessary in such cases.
Brake Pad Maintenance Tips
To prolong the life of your brake pads, follow these simple maintenance tips:
-
Regular Inspections: It's essential to have your brake system checked regularly to ensure your brake pads are in good condition.
-
Keep the Brake System Clean: Dirt and debris can affect braking performance. Regularly cleaning the brake system helps maintain its efficiency.
-
Avoid Overheating: Excessive heat can cause brake pads to wear out faster. Avoid sudden, hard braking and use the brakes properly to extend their lifespan.
Conclusion
Brake pads are a critical part of any vehicle’s braking system, ensuring safe and efficient stops. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of the pads help maintain peak performance, improve fuel efficiency, and reduce wear and tear. Pay attention to any signs of brake pad wear, and replace or maintain them as needed to improve your vehicle's safety and longevity.










